Refrigeration Condenser
Item Name Code (INC) 36880
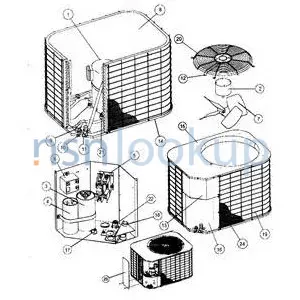 |
A self-contained heat transfer device which receives high pressure gas at temperatures above that of the cooling medium, to which the device passes latent heat from the refrigerant gas, thereby causing it to liquefy.
 Additional Information for Refrigeration Condenser
Additional Information for Refrigeration Condenser
Refrigeration condensers are an essential component of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. They are part of the supply class Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Components in the supply group Refrigeration, Air Conditioning, and Air Circulating Equipment.
A refrigeration condenser is responsible for removing heat from the refrigerant gas and converting it into a liquid state. It plays a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle by facilitating the transfer of heat from the system to the surrounding environment.
The condenser receives high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant vapor from the compressor. As the refrigerant flows through the condenser, it releases heat to the surrounding air or water, causing it to condense into a liquid. This process is known as condensation.
There are different types of refrigeration condensers, including air-cooled condensers and water-cooled condensers. Air-cooled condensers use ambient air to cool the refrigerant, while water-cooled condensers use water as the cooling medium.
Refrigeration condensers are typically made up of coils or tubes that allow the refrigerant to flow through them. These coils or tubes are often surrounded by fins to increase the surface area for better heat transfer. The condenser also includes a fan or a pump to facilitate the movement of air or water for cooling.
In summary, refrigeration condensers are vital components in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. They help remove heat from the refrigerant, allowing it to condense into a liquid state and complete the refrigeration cycle.
 Related Item Names for INC 36880 Refrigeration Condenser
Related Item Names for INC 36880 Refrigeration Condenser
 NATO Stock Numbers with Item Name 36880 Refrigeration Condenser Page 2 of 3
NATO Stock Numbers with Item Name 36880 Refrigeration Condenser Page 2 of 3
- 008312192
- 67-26428
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839SZ8-6
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 008312162
- 67-39009
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 810-1385839SZ16-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 008247495
- 67-31848
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 467-30788C
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 008190133
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839SZ8-6
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 9W70-109
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 3307387
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 008190132
- N12005-1PT9J4-154
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- S5901-3179746PT9J54-154
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 008179578
- 9W70-109-9W80-109
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839SZ8-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 3307387
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 008179574
- 9W70-109
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 3307387
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 008055498
- 67-36255
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 810-1385839SZ10-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 467-36234C
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 007998142
- 26H5-614
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 26H5-1233
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 26H5-614
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 007939744
- 025V242
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 025V242
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- S-5M
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- C-534
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 007625406
- 467-74946D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839SZ6-5-26
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 007529711
- 3307393
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 810-1385839SZ16-6
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 006310111
- 8664-236
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 8664-236PCASSYD
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 004933472
- 467-74937D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839SZ10-6
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 004785722
- 13216E6126
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- TIP01845-200CT71
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 004656224
- 91Q2A3321N7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839SZ10-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 9W90-179
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 9W90-179
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 9W10-179
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 004054908
- 9W120-179
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 9W10-179AND5820E5892N2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 004054910
- 9W60-409AND5820E5892N4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 9W60-409
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1
- 004011736
- 91Q2A3321N8
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 9W60-179
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 9W60-324
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 003952902
- 194105PC1T017
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- AVP10S59-159PC1T017
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 003684512
- CA68S5902-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 0MEA174-11
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 0MEA174-11
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 003555211
- R35166
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 53216S5901-1460
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 53216S5901-1467
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 003555191
- N12001-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 52208S5901-596983
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 003555195
- N12000-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 0ME145-11
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 3ME465-11
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- DD692S5901-13
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 52208S5901-596984
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 002898287
- N12157-1PT9J10-364
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 002891335
- S66C59500-439
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 002746382
- N12053-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- S5901-3170492
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- N12053-1-9J5-474
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 002728979
- 9J3-324
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 3125376PC1T015
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- N12251-1PC1T015
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 002704473
- 51200S59-836
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 423819
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 002704478
- 51200S59-837
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 403022
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- S5901-586939
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 423832
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 002566462
- 21058
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- DS408R1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 002558769
- 186075PC1T015-19T021
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 467-76865D
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 212-59-05PC1T015-19T021
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 066-07647ASSYN0 466-10889C
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1
- 002504877
- 91Q2A3321N6
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 9W91-179
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 002504876
- 91Q2A3321N4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 9W101-179
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1
- 9W101-179
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1
- 002045703
- J12-4-12-16
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- J12-4-12-16
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- DSP329
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 001226069
- 9W10-179
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 81Q2A3307N2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 9W70-179
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 001191265
- D2354
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- LMF166-2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 000895769
- 9W120-109
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 000895747
- 9W110-109
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 000895740
- 9W50-109
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 000886776
- R4120D159
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- R4120D159
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- R4120D159
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 010991518
- 13770
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 013770
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1
- 123762369
- 5436-830000C00C
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015756953
- 09R457A
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- LFH-0901
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 000222816
- 67-36305
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 810-1385839SZ6-4-26
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 810-1385839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 67-36305REVE
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 012737209
- 031A086
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 014587029
- 048935
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 015916275
- V300-24V
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016462804
- 77R1604
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- RD-4-5498-0P
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 016011285
- 736-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 015179473
- 066-0304-00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015931720
- 4285246
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015537766
- AT312058
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- AT312058
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- AT312058
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- AT312058
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- AT312058
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 015596100
- NTEC02-3-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016606064
- 61957
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015747606
- 9141126-01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016503305
- 330-0003
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015518897
- SW1-1/2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- CW1-1/2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 015765680
- MHX-602B-4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015538504
- 1834-428-34
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 1834-428-34
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 1834-428-34
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 016911916
- JAL-A101-CAV-020
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016700305
- 90C02-1182-34
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 014778126
- 7-511A21507-3
- RNCC: 1 | RNVC: 2
- E131007000-01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016825904
- 00PSY110176700
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- XW-0502-CAUS
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 015771766
- 3696278C1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 014437223
- 1074892
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015278987
- RD-4-5122-OP
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015733796
- NTEC02-1-2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015836030
- 150516-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 013724659
- 9W120-104
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015310646
- 70004-119
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 52C9594-17
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 015440450
- 20702
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 014437224
- 1076732
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015806383
- S-3 CN3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016155826
- 969197D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 969197D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 969197D
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 015904818
- 10011652
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015401456
- 90C02-9212-32
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- MHX-602D-4
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 90C02-1182-32
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 015303717
- 91196568
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 014905644
- 9W91-129
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015133206
- CN5/2H
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 014810753
- MSE-4005Z
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 013089911
- MS-150
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 013356389
- 620262-00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- RAR0665
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2
- 011243370
- 2674-6
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 013032369
- 09RP027-364-17
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015154313
- 620420 00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015822457
- 1E005994
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 1S005994
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 2591698C91
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 013647571
- S3193
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015508316
- KV23812
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- KV23812
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- KV23812
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- KV23812
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- KV23812
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 016751332
- CR18K6E-PFV-875
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016713943
- EB3B19710AA
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 7423175665
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 23175665
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 014806717
- 376-88631-000
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016245134
- RD-4-6901-0
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- RD-4-6901
- RNCC: D | RNVC: 9
- 016155824
- 971201D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 971201D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 971201D
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 011976803
- M10 115V AC
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- M10
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 015931721
- 4285247
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015924244
- 67-1763
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015869242
- MSTX 45-2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 013527237
- 9W90-703
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015822622
- SW 1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 013082791
- QMS-40-610M-4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015206183
- CN4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015505523
- CRX-603B-4P
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 003554644
- 186032
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CV22S59-14
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- CL106S5900-476733
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 186032D
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 186032C
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 014905643
- 9W70-129
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016808854
- TWE050CA50D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015517083
- 180-5927
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 180-5927
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 016772602
- NFC-107Q
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 014663110
- RD-4-5287-0
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 013706890
- 101-437
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 015596092
- NTEC02-1-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 015538489
- 1834-202-28
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 1834-202-28
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 1834-202-28
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 011943322
- 200
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 016921112
- F620420-00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 004011735
- 91Q2A3321N5
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 007939743
- 025V139
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 025V139
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- C234
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 014378988
- 4P4005
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 011568035
- RSW 2000-U22
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 171235353
- 8402-205
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 332035578
- 32101202
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 991000625
- LW22118
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- FV212166FV212174FV212421FV21235-
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 144745288
- 35229
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151871944
- 022051OR
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A3980022051OR
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123548153
- 858303001
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270200274
- AE170AD
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 11051YEL024
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 270134934
- 2C16 19710 AA
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 144326727
- 09ZZ3417 874EE
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 09ZZ417874E
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 145636791
- 15791
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 991322419
- S-CB5136-15
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- HB6-150-2CCB
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- 144472868
- M25Q25CD36T6N12002X6C
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 121588250
- 681715364
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 15364
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123782180
- K1353TB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145256620
- 20 242 031 1380
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144297945
- GRD75
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123821433
- 81619206038
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 9016904A
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 81.61920-6038
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 270084107
- F25/20500
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145429959
- C3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123379421
- 63640405
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 40186089-06
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 3640/405
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 144642748
- 789-0013
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 143736161
- 7380-46
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 143924593
- 0610052
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145437944
- 9302293
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 331066541
- FA378500B
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123557034
- 298160385
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 992576692
- 30/926127
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 152053891
- MHX-604D-4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144006592
- 192-80-06
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 997466645
- M-1433-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- AP6
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145570402
- 9215-0359-00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CVI 103
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 0035925
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 171091687
- 71-92-106
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- HBX16-260-2CIB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 171130109
- 71098094-BLAD2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- HBX6-80-4CIB-7552-A-2/3/4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 171088025
- 71.91.090
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- C/71/4297V-6382/710600
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144027627
- 9760-116
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 143956619
- 785-01200
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 332048116
- 302X09
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270109088
- 99999-NIIN-DA0029143
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 123104061
- 10468
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 143844475
- NO PRIMARY REF14-384-4475
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 620288-00
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 144847013
- 0K072/D1013
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 0K072
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123520756
- GLZ9300546
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 218921106
- 67-14432SN28A4S
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123089789
- K25-50WT
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123469564
- 2500238-041120.000.0
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 996679605
- 2 0143-443
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 44 7597
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144469892
- CEBV615
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 140312883
- 9760-115
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 123585057
- 63641046
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 0492242692-02
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 3641/046
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 219145373
- 10638578
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 121996020
- K 070 HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- K070HB
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 0K070
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 270558616
- 8C1619710AA
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 270134931
- 3C4619710AA
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- YC1H 19710 BA
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 171127084
- HD-6-33-2CIB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 142861811
- 61410F
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 171025528
- HB10-185-2CCB SPEC
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 332041163
- CD3818CC6F19T453L
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- M502093200000
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1
- CD3818CU/CU6F19T453L
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123932249
- 1030105-259080.000.0
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 226169667
- 237575
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144856665
- 96136352
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145080277
- NO PRIMARY REF14-508-0277
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 86248N020113
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 123556897
- 64416123
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270252283
- Q23-74
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145598479
- 10211-3000
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 171109255
- HB-7-185-2-AIP
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 992160509
- 14557933
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- VOE14557933
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- CV185983
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 991522043
- PUHZ-P100VHA3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270381136
- HS 25
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 982060139
- K-002-015
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 982049545
- 202321-01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123239745
- K072HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- K072HB-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 123110669
- K071HB6
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 994413503
- 30/926448
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123116826
- 0401061014-07
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 0401061014-07
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 332087447
- 1AMET/AC-193A3/1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 375159921
- 83020560
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 83020560
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 83020560
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145670460
- 7421355240
- RNCC: 1 | RNVC: 2
- CVI104
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145663560
- Y00012476
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145579942
- AA1235F01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151938685
- 42N-07-11130
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)AH72442N-07-11130
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145249012
- 233201
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 171191208
- 2010109
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123494009
- K033N
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145354889
- 427242
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CL090368
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9
- 123485106
- K032NB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 0601
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 30090301/02 ITEM 12
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 30090301/02/12
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145422087
- 571869008
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 571869008
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 144510549
- CEBV490
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123133299
- K121H
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123452111
- K2922TB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- K2922TB
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- K 2922 TB
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- K 2922-TB
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 226174345
- 14594638
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145707890
- 07CO27
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145392416
- 100550D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270375757
- 83A00-76702-AA
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145770945
- AA1373F00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 375122449
- Q65082420
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- Q65082420
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 219023007
- DDC-64
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 1
- 123424153
- 63641011
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 3641/011
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 151883582
- 7104420
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145772435
- 14004279
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 171100895
- 283.002.210.101
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144574744
- DORIN-OCV01101
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 332067873
- 6029020042
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 6029020042
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 6029020042
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145038489
- CONDARIA/SMC800-8T
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 23PEPB/070322-002.PL-7/7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123546963
- 121 0004
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270558615
- 7C1619710DA
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 123797742
- 05579238
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CV168783
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 05579238
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144750700
- 194329151
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 170457876
- 47074HB6IN100-4CIB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144023874
- 785-0120
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 150012545
- 99487944
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 993523924
- 326L61029-M01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 002594428 ITEM 2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 002594428/2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 426L61084-M01 ITEM 2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 426L61084-M01/2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 002594428/AS/2 ITEM 2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 002594428/AS/2/2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 002594431
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 991480236
- 92050
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144669493
- 92136A0023
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 996766682
- 2/UFD10308/1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123841334
- 81619200011
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 81.61920-0011
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123870021
- K123 HB2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151809975
- STMPX22744
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A9366STMPX22744
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144865091
- H118140
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145717451
- AA1402F00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 14100083395
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 251495286
- 8550 02702
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 855002702
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 1503959
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 226155767
- 600073
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145583654
- UP450.13
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123673922
- 858303801
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145475840
- D1360048
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 143062039
- NO PRIMARY REF14-306-2039
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CASH30
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 190046935
- GCIPR001501
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145090131
- 43121463
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144750555
- CFM312-124
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 150023564
- CFC/M 30
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145756598
- 7422053970
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 7422053970
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 22053970
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123314989
- K 122H
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- K122H
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- RAB0561
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- K122H
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 121674910
- 681717003
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 03-681717003
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 17003
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 190046936
- GCIPR001502
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123769494
- 64293398
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 375227614
- A50044911
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- A50044911
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145372591
- 7SP032017
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 992608808
- 8001980489
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 992535159
- 92077
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 170457877
- 47075HB6IN100-4CIB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145654603
- 87063
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145299426
- CEBV235
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144899814
- COND140/VAL
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 992389388
- 2001095
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 332079487
- 980814
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CL0020
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123873642
- K1053H
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 996019895
- GLY10435
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 7421611420
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 21611420
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 998870441
- CONDE00024
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 996629192
- 525690
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 998128659
- R051
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 013651B
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 270070020
- SK30225
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 171128661
- HD5-12-033-2CCB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144354173
- 2076210
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 340389125
- 589560014
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 589560014
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 589560014
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9
- 123318399
- 70.362.05.405
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 00009192670
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 09192670
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 145606175
- 3030188975
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- R7137766
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- CV149997
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- R7137766
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 991496833
- GLY2273
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- AS54852
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 2273
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9
- 144700614
- 8337208
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 734862704
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123556660
- 63641045
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144609771
- 46061656
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 46061656
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 121674915
- 681714246
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 14246
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 310142075
- 107823310
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270529880
- KONDANSER
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270596399
- 10T BZBOX
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 145163200
- 21138-H000101
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 661290178
- 2TM24/2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 991871873
- COND 290
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123536859
- K073HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123471609
- 298559223
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 661611045
- CRKC 502320
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 142627647
- F242A
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123933287
- 8516989
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270482212
- 51RS980179
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 144448214
- 6508-3-01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- FM250-4-18
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- FM250-4-18/6508-3-01
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 998788705
- GLY 9362
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123729462
- 7084900
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144574754
- ASPERA-9-660-438-138
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 993868288
- 30/926494
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 30/926494
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145280437
- 3017
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123904474
- K373HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- K373HB
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123765178
- 5000-E011
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145375372
- AA1225F00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144646996
- 427104
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144684338
- CERH1800
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- RAR0711
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145190249
- 7052A32-190-02
- RNCC: 1 | RNVC: 2
- 120-0350-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 332079485
- 225159
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145278596
- TGDC1603
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 171127076
- 2XHE6-33-2CIB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 226244273
- 0745658
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 226200265
- 063121
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123682305
- 7074002
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145020299
- 425067
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123923968
- 56E0721132
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 996418796
- WCV015
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145730847
- SPP2750088
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145766565
- 10724367000
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 251605856
- 88460-60400
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144844779
- 91140-100
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 91737640
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 91737640
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144574760
- ASPERA-20MFD400V
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 123760518
- 1556347
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 997086643
- QMS 0804/1199/S1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- LF-40252
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- QMS 0804/1199/S1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 142768679
- NO PRIMARY REF14-276-8679
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 1C0063
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 123551157
- K203HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 143147668
- TC35-4RANGDR0IT
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 580003926
- 004505
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 004505
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 10312229
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9
- 123104062
- 10457
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 310142802
- 20495950810-00
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 997961713
- N.1O19.
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 121480051
- MY1212505R2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- MY1212505R2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123870020
- K203 HB2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 991760521
- BDC143B300
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 190046937
- GFEPR001501
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 580003356
- 705512
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 705512
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144191135
- 79121251
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 79121251
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 145549340
- 1790840
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151447882
- 160T-150-CUNI-RXB70
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 993746771
- GLY1201-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- FV 2067028
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- FV 2067028
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145118779
- 400785
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 121498092
- NO PRIMARY REF 12-149-8092
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 5133Z
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 226165939
- 6000500
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 226160451
- 4B1 820 103
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123774831
- 64293813
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270599615
- EWC 50
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 144882699
- 17945
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 996615569
- FV 2194318
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CAC 103 A19
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- CAC 103 A19 ISS G
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 143930532
- 10270-88
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 123621321
- 024.05600
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 553191708
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 151934277
- 76092221
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A398076092221
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144802099
- GFEFA06
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- F2210020
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 145329954
- 10654825
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 332035579
- 32101203
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144203382
- CERHM100
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 992283930
- 2477001
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 121480050
- MY1212505R1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- MY1212505R1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144849006
- 189307-156R
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 123625635
- 4635000654
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 142959784
- 09DC16-703-15339-32286
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145427543
- 50061532
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 661522680
- D-0892
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145280436
- 3013
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 190020610
- TCB0012D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145090132
- 43121464
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 121927669
- 858400501
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 190020609
- TCB0008D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145306241
- 8338208
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151495513
- KA150
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151986347
- 2103.3004
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A49782103.3004
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- W111133P1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145358518
- 941221011
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123424154
- 63641008
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 3641/008
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 145475872
- D1360045
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145475859
- D1360044
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 143473532
- S3Z5301555000
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145558311
- 19213768
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 189810300
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 997937553
- G98928
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 11A0/132576
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 320846994
- 2000891583
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270372831
- 430100672
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 375146791
- 60821850
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 60821850
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- KDS 2350-4002
- RNCC: 4 | RNVC: 1
- 151930523
- 8500878
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A39808500878
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 219216389
- 9660417-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145411029
- 100549C/100550D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 18784030-0
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 18784029-8
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145024513
- 423090
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144264368
- 8412412400
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 8412412400
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 993826568
- EV4952
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- GL60PBJ5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144535980
- 4772205040
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 5044154
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 994189320
- AA-2776-400
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 661602528
- 110604
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- BMA-H16-0003-01
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145475845
- D1360049
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 331066544
- 0353101X04
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151569341
- 234
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 1PA424942535144
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 234
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 42535144
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 151996829
- 99436213
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A424999436213
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 661508305
- 836-48-6M
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 332027673
- 6453C7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 143878258
- 300148824
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145425343
- B3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145253038
- 8338205
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 833205
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 145434918
- F118140C
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145358517
- 941221000
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151990016
- 2181.3001
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A49782181.3001
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123487999
- C 5000573
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123531338
- K 813 HB-4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 997260433
- FV 2261971 ISSUE C
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145467802
- 91187518
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123634993
- 63641062
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145349091
- C2AH270S6P
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CL090436
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9
- 145038951
- 41
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- F2209900
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 144595534
- 89218121000
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144899820
- SCREW370/VAL
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123825748
- 64293882
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 64293882
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144769930
- 7181131A
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 200076001
- 10700615-001
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 10700615
- RNCC: D | RNVC: 9
- 123632088
- K123H
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151559326
- 303050074A
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 60185771
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 303050074A
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 270109085
- 99999-NIIN-DA0029142
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 270581090
- 202116
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145453563
- KSV 016 Z 251 C
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- AA013221
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9
- 991523799
- N.1077
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 143999081
- NO PRIMARY REF14-399-9081
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 028-4201
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 310142074
- 107823300
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144317936
- TCPV17603
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 268076-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 145259754
- 50108070
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144802189
- 18551E001300
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 219081406
- 1140-070-01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 1140XXXX04001009
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 8605134
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123330428
- 5 000 146
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144574738
- DORIN-OCV00150
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 995662454
- B45016
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151952077
- 022446/1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 0400-0391
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 151933054
- 42538724
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A424942538724
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 151996966
- 504022659
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A4249504022659
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 121726901
- GLZ1315193R1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 226129923
- 15815036
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 0511337
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 151934178
- 8920827
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A39808920827
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144003798
- GC142
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 85-692-7795
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9
- 270252280
- 160X1C
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145148041
- 8337223
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144735021
- 11-851655
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 998463160
- 326L62087-M01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 002594455
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123379422
- 63640403
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 0401061014-08
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 3640/403
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 123933299
- 8519284
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270518669
- 51RS980267
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144469862
- CEBV375
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- CEBV375
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- SYB1769
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 997624756
- 1379D000
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144674500
- 312-03141-501
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 312-03141-001
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 190020608
- TCA00242D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145427191
- UC73A
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123725387
- K283HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145054957
- 5010175322
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270252281
- 295X2C
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145609258
- 504241
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145619533
- F00380412
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144846968
- Z68323A
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144587611
- 425064
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- RAB3048
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123622029
- K073H
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270200271
- AE650AC
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 11051YEL020
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 151959029
- 64539229021
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)AB67764539229021
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 143832380
- 001
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 992553196
- FV2110634
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- FV2110634
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145442491
- 200656
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 143147671
- TC3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144263936
- 9023CPV6113A
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123058247
- K 201 HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 661525476
- 4488 W
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123458468
- 5 000 089
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- WGB:5000089
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 144587482
- 425085
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- RAB3084
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 170457875
- 47073HB6IN100-4CIB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123278511
- 20987
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144931375
- NO PRIMARY REF14-493-1375
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 10250-153
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- F300 0T 010 5338
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9
- 151885017
- 1022C1603040021001(1+1)
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 661360260
- MS150003
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 399A02452002
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 270252352
- QR3-44
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145474944
- D1360050
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151591423
- PN UAS 00008082
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 6760F76004835
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9
- 270200272
- AE547AD
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 11051YEL022
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145358508
- 940685000
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 142949566
- 2632
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123774604
- 64293808
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 142949567
- 2633
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151989979
- 2180.3001
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- (241)A49782180.3001
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 145198325
- K9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 9
- 661413853
- D50682
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 151790778
- CS00001601109
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123133300
- K071H
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123170963
- K121HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 270200273
- AE1000
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 11051YEL023
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 144236494
- CHS2712C
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 332018967
- 100433020003
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 142824456
- CECC6000FGH
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144901572
- 960510301
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145642421
- 10643619
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 190012691
- CFA-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 152058546
- 5801346522
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 144161312
- 230683
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123871350
- K1053HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- K1053HB
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 226124095
- 600978
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123234949
- K122HB
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- K123HB
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 516103
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 270292864
- F25/20562
- RNCC: 2 | RNVC: 1
- 145277492
- 708951
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 331066537
- FA1063400
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 145445983
- 849252D
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 7700272626
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123611500
- 29.02698
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 123107848
- 74.80004-CUNI70/30FE
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 74.80004
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 123802020
- 4375000054
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 991347985
- MS1810/1201
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2
- 226L65277-M00
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2
- 661244964
- ASB219
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2