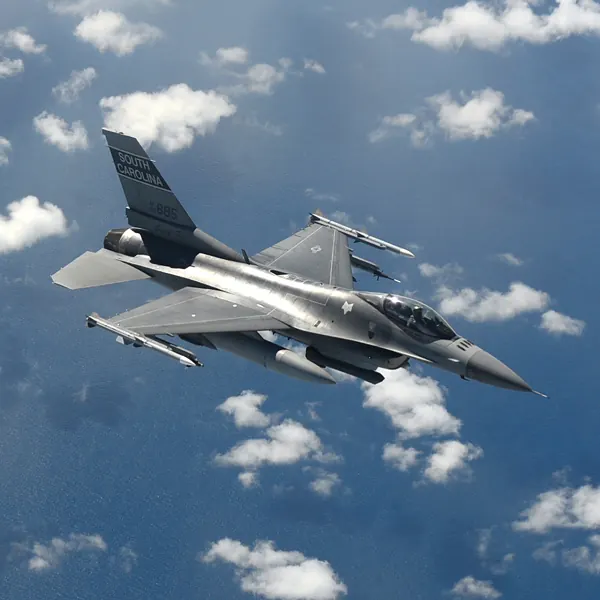
F16 Jet Fighter Aircraft
Multirole Single-Engine Fighter
Page 2 of 315
The General Dynamics F-16 fighter aircraft was originally developed in 1973 as a daytime conditions air platform to provide air superiority. Over 50 years of service it has evolved into a capable all-weather multirole aircraft. As of 2023, more than 4,600 aircraft have entered service and there is still limited production for end users other than the US Air Force.
F-16 Fighting Falcon Features:
- Single-Engine
- Highly Maneuverable
- Supersonic
- Lightweight Fighter Jet
- Fly-By-Wire
Primary Variants:
- F-16A Original (Single Seat)
- F-16B Original (Two Seat)
- F-16C Block 25, Block 30, Block 40, Block 50 (Single Seat)
- F-16D Block 25, Block 30, Block 40, Block 50 (Two Seat)
- F-16E Block 60 (Single Seat)
- F-16F Block 60 (Two Seat)

 F16 Technical Specifications
F16 Technical Specifications
General Characteristics
- Crew
- One or Two
- Dimensions
- Length: 49 feet 5 inches (15.06 meters)
- Height: 16 feet (4.9 meters)
- Wingspan: 16 feet (4.9 meters)
- Weight - Takeoff: 42,300 lbs (19,187 kg)
- Weight - Basic: 18,900 lbs (8,573 kg)
- Height: 16 feet (4.9 meters)
 F16 Technical Specifications
F16 Technical Specifications
Mobility
- Propulsion
- Single General Electric F110-GE-129 (Block 50)
- 29,500 lbf (131 kN) thrust with afterburner
- F-16 Top Speed
- Mach 2.05, 1,176 kn (1,353 mph | 2,178 km/h)
- Ceiling
- 58,000 feet (18,000 meters)
- F16 Range
- 500 miles (860 kilometers)
 F-16 Technical Specifications
F-16 Technical Specifications
Functional & Cost
- Primary Function
- Multirole, All-Weather, Fighter
- F-16 Cost
- $18.8 Million (USD)
 Biography of the F16 Jet Fighter Aircraft
Biography of the F16 Jet Fighter Aircraft
The General Dynamics F-16 fighter aircraft was the US Air Force's Fourth Generation daytime conditions air platform to provide air superiority. Over 50 years of service it was developed into a capable all-weather multirole aircraft. As of 2023, more than 4,600 aircraft have entered service and there is still limited production for end users other than the US Air Force, such as Taiwan, Bahrain and Slovakia. The F-16 Falcon Block 70 aircraft are the first production version for Bahrain.
The latest F16 Viper provides all-weather multi-role fighter operations. The F-16 Viper is fitted with an internal M61 Vulcan Cannon and has eleven external armament mounts. The F16 can carry many types of ordnance including AIM-9 Sidewinder, AIM-120 AMRAAM, AIM-7 Sparrow, Electronic Countermeasures (ECM), Bombs, Navigation Pods, Targeting Pods, Weapons Pods and External Fuel Tanks.
The F-16 Falcon was the first production fighter aircraft intentionally designed to be slightly aerodynamically unstable, also known as relaxed static stability (RSS), to improve maneuverability. Most aircraft are designed with positive static stability, which induces aircraft to return to straight and level flight attitude if the pilot releases the controls; this reduces maneuverability as the inherent stability has to be overcome. Aircraft with negative stability are designed to deviate from controlled flight and are therefore more maneuverable. At supersonic speeds the F-16 gains stability which eventually becomes positive because of aerodynamic changes. The F16 top speed is Mach 2.05.
In an air combat role, the F-16 falcon's maneuverability and combat radius (distance it can fly to enter air combat, stay, fight and return) exceed that of all potential threat fighter aircraft. It can locate targets in all weather conditions and detect low flying aircraft in radar ground clutter. In an air-to-surface role, the F-16 can fly more than 500 miles (860 kilometers), deliver its weapons with superior accuracy, defend itself against enemy aircraft, and return to its starting point. An all-weather capability allows it to accurately deliver ordnance during non-visual bombing conditions.
The F16 cockpit and its bubble canopy give the pilot unobstructed forward and upward vision, and greatly improved vision over the side and to the rear. The seat-back angle was expanded from the usual 13 degrees to 30 degrees, increasing pilot comfort and gravity force tolerance. The pilot has excellent flight control of the F-16 through its "fly-by-wire" system. The pilot wears a flight suit, gloves, boots and helmet designed specifically for the Electrical wires relay commands, replacing the usual cables and linkage controls. For easy and accurate control of the aircraft during high G-force combat maneuvers, a side stick controller is used instead of the conventional center-mounted stick. Hand pressure on the side stick controller sends electrical signals to actuators of flight control surfaces such as ailerons and rudder.
The F16 Falcon was built under an unusual agreement creating a consortium between the United States and four NATO countries: Belgium, Denmark, the Netherlands and Norway. These countries jointly produced with the United States an initial 348 F-16 jets for their air forces. Final airframe assembly lines were located in Belgium and the Netherlands. The consortium's F-16 jets are assembled from components manufactured in all five countries. Belgium also provides final assembly of the F100 engine used in the European F-16s. Recently, Portugal joined the consortium. The long-term benefits of this program will be technology transfer among the nations producing the F-16 jet, and a common-use aircraft for NATO nations. This program increases the supply and availability of repair parts in Europe and improves the F-16's combat readiness.
US Air Force F-16V Viper multirole fighters were deployed to the Persian Gulf in 1991 in support of Operation Desert Storm, where more sorties were flown than with any other aircraft. These fighters were used to attack airfields, military production facilities, Scud missiles sites and a variety of other targets.
During Operation Allied Force, US Air Force F-16V Viper multirole fighters flew a variety of missions to include suppression of enemy air defense, offensive counter air, defensive counter air, close air support and forward air controller missions. Mission results were outstanding as these fighters destroyed radar sites, vehicles, tanks, MiGs and buildings.
It has been discussed within NATO in 2023 that the F16 plane could be deployed to the Ukranian Air Force in support of the Ukraine / Russia War.
F16 Weapon Systems Designator Codes (WSDC)
- BUF - F100-Pw-200 (F-16A / F-16B / F-16C / F-16D) Aircraft Engine
- 26F - F-16 Aircraft
- 47F - F-16 Simulator
- 92F - F-16 Aircraft Support Equipment
- N4F - F-16 Ne Special
- BVF - F110-Ge-100/129 (F-16C / F-16D) Aircraft Engine
 F-16 Viper Spare Parts
F-16 Viper Spare Parts
Weapon Systems Designator Code (WSDC): BUF, 26F, 47F, 92F, N4F, BVF
AIRCRAFT, F-16 NSN Parts for F-16 Viper Aircraft Page 2 of 315
NSN Parts for F-16 Viper Aircraft Page 2 of 315
- 1560PL0856384
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16B1305-801S
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 6
- 16S919-5
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16L319-47
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W380-177
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W380-172
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W380-171
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4622-4
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B4623-609
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6312-126
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6312-135
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16P1911-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S1709-8
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S1712-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B866-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B1813-17
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B5549-27
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5549-51
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1314-21
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16B6577-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B5514-39
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B5162-19
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6868-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6864-15
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16T9197-11
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0658552
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16K0035-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4450-19
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16K0612-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6207-39
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4450-22
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16T9194-803
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4623-608
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6322-21
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16P1562-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 53042BP106
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6864-11
- RNCC: E | RNVC: 8 | DAC: 2
- 16W191-19
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16W198-21
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5304-805
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0659262
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 39070-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W191-21
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 6156302
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 5
- 320-4-45588-109
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 320-4-45589-103
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 320-4-45838-101
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W380-109
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16S1304-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6312-83
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0653364
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 5330PL1843298
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16B6804-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6804-8
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL1843341
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16B6575-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6312-101
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6312-100
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S1704-19
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1763-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B861-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16P1911-2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S1704-13
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S1704-14
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16S1709-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S1712-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B5891-13
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0658546
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 2-300-01307
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- CR3-3116-502-.0015N.6.1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16T9167-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16T9196-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 27-370-20784
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0659251
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 1560PL0659252
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 68A230091-1019
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5527-29
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- C7976BP098
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W380-138
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0653372
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16Y161-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 27-370-40005
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 27-370-40064
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 27-370-4986
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0659259
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16B5550-21
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B6130-21
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16W191-22
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16H1908-41
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16B1878-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16E3148-15
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0653379
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 320-4-45513-101
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 320-4-45539-101
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 320-45541-101
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 6
- 320-4-45542-101
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 320-4-45587-103
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W380-142
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6553-802
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4505-39
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 5
- 16B4505-53
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 2
- 202C221-13-0
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W382-119
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 5-96330-250
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 6
- 16T7402-71
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6312-85
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6312-84
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6280-28
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S1704-22
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16S1712-14
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6804-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- P5119-2-2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4825-30
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16B4825-35
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16B1764-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 32-21150-75
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5842-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 70305-02105-043
- RNCC: 1 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 1560PL1621793
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16T7244-803
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0659250
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16T7242-807
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16T9192-55
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4602-9
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4601-23
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4450-20
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4601-21
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6579-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 2-300-20698C
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 6
- 343603-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1540-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4623-603
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 27-370-40022
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16W382-118
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16B6130-37
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B4615-17
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 27-370-4987
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 2
- 27-370-40039
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16M031-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0653376
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16P408-805
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6861-79
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16E3147-13
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 7032128-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16K0640-12
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 4
- 16K0640-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 4
- 16B6825-26
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6825-15
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16W382-120
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 27-370-20667B
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 4
- 64-1070-39
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1685141-93
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B5141-25
- RNCC: E | RNVC: 8 | DAC: 2
- 16B6308-16
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 352863-6
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0659891
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 1560PL0659895
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16F2184-51
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W265-27
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0659896
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16B6807-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16K0662-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0659901
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16B4233-803
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4233-1
- RNCC: E | RNVC: 8 | DAC: 5
- 16B6801-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W285-14
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W044-7
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B7204-13
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 2-300-20844
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W283-50
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B40011-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B40011-24
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B40601-25
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B40601-29
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B40602-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B40620-19
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16T7465-4
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16B6886-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6886-79
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6886-39
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6542-21
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W130-30
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 6064T38G01
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 2-300-21092
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W042-22
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 160D712507-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16W125-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0917446
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16W294-15
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16W173-5
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W282-17
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0654000
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16W380-165
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16F0181-839
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W1262-19
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- L5235016-001
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16T9190-25
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1835-827
- RNCC: E | RNVC: 8 | DAC: 2
- 612R467H01
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 12293498
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 6
- 12293422
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1 | DAC: A
- 12293454
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- TR 70230-50
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 6
- 6-82047-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 5
- 7132971-10
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 7132966-01
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 2659517
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 2658563
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 293BC440030
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 58A119D111R
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 32-94654-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 7132956-01
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S303-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: A
- 201113843-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S217-10
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S217-9
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 7132912-30
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S307-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 3365531-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1440PL0916679
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16S222-5
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 4
- 3365504-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 3365810-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S252-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16S210-19
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 5
- 16S212-51
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: A
- 704AS4167
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 704AS7087
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 704AS7088
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S210-503
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 704AS4002
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 68A733180-1005
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 8326401-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 7002795-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 7002570-8
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S1553-12
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S1553-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 7002545-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: B
- 16S212-61
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S1535-13
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S1551-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 7002594-2
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 7002768-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S258-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16S1515-809
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 7002795-2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 7002603-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 5
- 8984116
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 7002552-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 9030056
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S1560-803
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 68A733033-2019
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 7002566-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 7002190-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: D
- 3825236-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 7002571-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 7002791-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 7002762-4
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 48029
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: B
- 704AS10899
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: A
- 7002731-4
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: D
- 704AS4003
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 64A97D12-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: A
- R97945
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 6
- 320AS104-20
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: A
- 20666-4-2
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 639AS1373-2
- RNCC: 7 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- HY0941/1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 639AS2781
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 10162785
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 8858T3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- NAS1149CN832R
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16C139-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B1220-607
- RNCC: E | RNVC: 8 | DAC: 5
- 16T4629-9
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 2
- 16T4629-10
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 70217-01024-042
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16B1837-819
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0658480
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16W384-32
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W384-35
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 70217-02718-119
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16B1305-5
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1302-13
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 6
- 16K2621-18
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16K2326-827
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6530-80
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 5
- 16B1920-801
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4510-13
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 6
- 16S405-805
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1318-29
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S404-49
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B710-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16P1523-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4460-802
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4221-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1245-811
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0658486
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16P231-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 2-300-01428
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16P1888-5
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1835-811
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B5210-809
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B4220-4
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0853576
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 5040000-002-101
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- L-39219-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4872-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: A
- L-39221-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4871-11
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4226-6
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16T7480-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 70217-02718-063
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16T4670-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16F0143-811
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4620-27
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16F1103-5
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16F0195-5
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y368-5
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1235-823
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B1235-829
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B1232-821
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B1837-101
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16D1700-753
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16D1700-751
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16D1700-759
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 68A334001-2033
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 70209-06012-101
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 1
- 1560PL1951819
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 70302-02152-043
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16Y379-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16Y382-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y383-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y438-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16F0115-3
- RNCC: E | RNVC: 8 | DAC: 2
- 16P1554-25
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16P1554-29
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4621-45
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4621-827
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16Y368-803
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W380-104
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y523-45
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL0658516
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16P1554-30
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 70216-01000-104
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 1
- 16B4624-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B2520-803
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4871-13
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16L113-802
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5513-31
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16K0322-16
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B6300-15
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1512-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16F0231-13
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4240-13
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 2-300-01375
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B5551-19
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5341-15
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 1
- 16B5250-871
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 4P32234-101A
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 6-72472-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: D
- 62D11075
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 32-12017-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- GHN10275-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 4
- 4P33216-101B
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL1742919
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 3329853-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 153C6250P1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- K000021-1001
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 6
- K000019-1001
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 160D950261-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0655081
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16W550-4
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 4F52302-111A
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 2
- 16W255-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W550-3
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W580-15
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W580-9
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16P154-9
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16P202-11
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 2
- 16W252-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S155-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 1560PL1625184
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 1560PL0658364
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16W289-7
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 2
- 16P276-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S132-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16M216-9
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16L134-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16L053-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16M210-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16M031-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16Y334-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S170-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W042-803
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 2
- 16H1705-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16S156-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16S145-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16P179-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16M044-9
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S136-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16M204-3
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 5
- 16Y464-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16Y465-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16S114-10
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16K0628-11
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16H956-15
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16K0059-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B2801-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y421-43
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16M204-802
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0658349
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16B1303-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4232-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1556-809
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4235-9
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16Y112-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y117-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1214-8
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y171-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W156-11
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL0653332
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- C7850-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16P190-16
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16W581-24
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16P103-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4825-10
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4440-21
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16L108-8
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16W581-25
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 1
- 16T7246-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16B6544-3
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16W581-21
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16P100-13
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16P140-3
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16W581-22
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6501-1
- RNCC: C | RNVC: 1 | DAC: 2
- 16B4825-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1510-90
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6568-34
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16B6552-9
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y236-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5533-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B5533-6
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y210-5
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6568-11AG
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 6
- 16Y210-37
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4821-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5841-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B6862-9
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B6867-13
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4232-801
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6868-7
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16B5853-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y334-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1945-9
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6580-11
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16B1822-62
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16P1522-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B1855-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1556-807
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6530-65
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B1822-51
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B1316-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5216-13
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6553-5
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B1837-3
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6312-28
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 2
- 16B1837-23
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6312-31
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B6321-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6312-35
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6321-12
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B2305-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6509-9
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B5181-11
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B1260-17
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1705-805
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1822-64
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16Y217-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16B4406-12
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B5801-11
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1822-65
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16Y217-15
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6863-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1945-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B2305-8
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1555-825
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B2305-9
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B4231-1
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 4P29094-111A
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B1311-13
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 6
- 16P1527-5
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 5
- 16B4231-801
- RNCC: 5 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 16S432-7
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6314-37
- RNCC: 8 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 5
- 1560PL1628655
- RNCC: 6 | RNVC: 9 | DAC: 9
- 16B6306-14
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2
- 16B6569-1
- RNCC: 3 | RNVC: 2 | DAC: 2